- What are MX Records and Why are They Important?
- How to Find Your Google Workspace MX Records
- Enter Google Workspace MX Records at Your Domain Registrar
- Verifying and Troubleshooting Your MX Records
- Differences Between MX Records for G Suite Legacy Free and Paid
- Setting up DKIM, SPF, and DMARC with Google Workspace
- Who Needs Google Workspace MX Records?
- Google Workspace MX Records and Changing Domain Registrars
- Troubleshooting Email Delivery Issues Related to MX Records
- Conclusion and Summary – Key Takeaways for Google Workspace MX Records
What are MX Records and Why are They Important?
MX (mail exchange) records are DNS records that direct incoming email to the servers responsible for accepting and delivering email for your domain. They indicate which mail servers are designated to handle your inbound and outbound email.
Properly configuring MX records is crucial for routing email correctly and ensuring messages do not bounce. Without valid MX records set up, email sent to your custom domain accounts on Google Workspace will not make it to the recipient’s inbox.
Key reasons MX records are vital for Google Workspace:
- Direct mail to Google’s servers rather than your domain registrar’s default email
- Ensure delivery of email for all accounts using your custom domain
- Reduce risk of messages being flagged as spam
- Prevent bouncebacks and non-deliveries
MX records specifically point to the mail exchange servers used in Google’s infrastructure and workspace environment. They enable seamless mail transport and act as virtual post offices for your domain’s email.
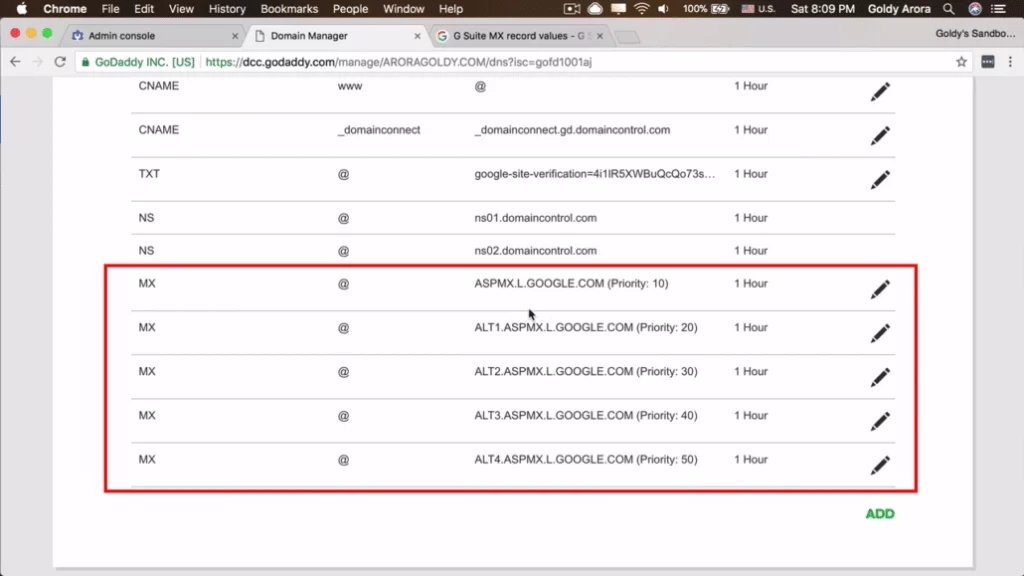
How to Find Your Google Workspace MX Records
Google provides the required MX records to route messages for your domain registered in Workspace. Here is how to locate them:
- Log in to your Google Workspace admin console
- Navigate to Settings > Domains
- Click the domain you want to view records for
- Scroll down to the MX records section
- Here you will see the default records that need to be entered at your domain registrar’s DNS settings
- Copy or write down these values – you will need to enter them exactly as shown into your DNS configuration
There are 5 MX records for standard Google Workspace accounts. Legacy free editions may only utilize 3 records.
Example Google Workspace MX Records
| Priority | Hostname |
|---|---|
| 1 | ASPMX.L.GOOGLE.COM |
| 5 | ALT1.ASPMX.L.GOOGLE.COM |
| 5 | ALT2.ASPMX.L.GOOGLE.COM |
| 10 | ALT3.ASPMX.L.GOOGLE.COM |
| 10 | ALT4.ASPMX.L.GOOGLE.COM |
The priority value indicates preference – lower numbers first. Each handles a portion of email traffic.
Enter Google Workspace MX Records at Your Domain Registrar
Once you have recorded your MX records from Google Workspace, you need to enter them into your domain name registrar account that holds and manages your domain. Here are the steps:
- Log into the account interface for your domain registrar
- Locate the DNS record or zone file section
- Add each of the 5 MX record values on separate lines
- Input the priority, hostname, and domain name
- You may also need to switch the nameservers for your domain to Google’s
- These propagate and direct traffic to Google’s infrastructure
- Save all changes made once complete
It can take up to 48 hours for newly entered MX records to fully propagate across DNS servers. Expect email delivery issues immediately after changing records until propagation completes.
Important note: If you change domain registrars or DNS providers, your existing MX records from Google Workspace will carry over. However, you must re-enter them manually into the new account interface to maintain seamless email delivery and prevent interruptions.
Verifying and Troubleshooting Your MX Records
After updating your MX records, it is important to verify everything is entered correctly without typos or other errors. Here are some tips:
- Use MX toolbox checker to validate records
- Correct any invalid or inaccurate entries in your DNS
- Confirm changes save if previously showing correct
- Retry sending emails if facing delivery problems after ~48 hours
- Double check differences if on legacy free Google Workspace plan
Common MX record issues include typos in hostnames, incorrect priorities leading to misorder, and omitted entries from the full list. Review closely and fix any identifiable mistakes.
For ongoing mail flow problems after MX records are showing correctly, you may need to troubleshoot with Google support to debug further.

Differences Between MX Records for G Suite Legacy Free and Paid
It is important to note the legacy free edition of G Suite (now Google Workspace) only utilizes 3 MX records, while fully paid accounts take advantage of 5 records.
Legacy free edition MX records:
| Priority | Hostname |
|---|---|
| 1 | ASPMX.L.GOOGLE.COM |
| 5 | ALT1.ASPMX.L.GOOGLE.COM |
| 10 | ALT2.ASPMX.L.GOOGLE.COM |
The paid Workspace tiers add two additional mail handler server records with priority values of 5 and 10. This expanded configuration improves performance and load balancing in the full production environment.
Check which plan you are on if your MX records from Google only list 3 entries.
Setting up DKIM, SPF, and DMARC with Google Workspace
Alongside MX records that route email delivery, Google Workspace also utilizes DKIM, SPF, and DMARC protocols to verify sent messages and prevent spoofing, phishing attacks, and other unauthorized use.
While MX records focus on mail transport, these complementary technologies authenticate your emails and domains for recipients.
Overview of DKIM, SPF, and DMARC Records
DKIM – DomainKeys Identified Mail signs messages to confirm they genuinely came from your domain’s servers. Prevents tampering.
SPF – Sender Policy Framework verifies sending hosts are authorized to send emails from your domains.
DMARC – Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance builds on SPF/DKIM to stop impersonation.
Correctly configuring these records is crucial for establishing trust, delivering email to the inbox, enabling authentication checks, and protecting your sending reputation.
Who Needs Google Workspace MX Records?
Google Workspace MX records are required for any domain names you want to send and receive email addresses with.
For custom domains added to Google Workspace, MX records are especially critical to:
- Route messages to accounts using your domain instead of the default registrar email
- Allow proper mail delivery for your email addresses rather than bouncing
- Avoid spam folder designations from authentication failures
In short, anytime you use a custom domain with Google Workspace – you need to point the MX records to Google’s servers. Without this mail exchange configuration, the email capabilities basically break.
Google Workspace MX Records and Changing Domain Registrars
If you decide to transfer your domain registration away from its current registrar over to a new provider, your existing MX records will remain unchanged.
However, because you have to manually re-enter DNS record values when changing registrars, it is important to properly configure the MX records identical to your current setup during this transition to avoid any email delivery interruptions.
The hostname values and priorities for Google Workspace do not alter when transferring domain registration ownership. But mail flow can stop if the records are not copied over accurately to the new account interface soon after the switch.

Troubleshooting Email Delivery Issues Related to MX Records
If you suddenly begin noticing email bouncing, not coming through, landing in spam, or other failures after formerly working – incorrectly configured MX records are often the culprit.
Here is an overview of debugging steps to isolate and fix MX record-related mail flow problems:
- Use MX diagnostics tools check if values changed or disappeared
- Look for DNS misconfigurations like priority order mistakes
- Review recent domain changes like transfers or account edits
- Contact registrar support if needed to resolve record errors
- Re-enter correct MX records from Google if somehow erased
- Clear email server cache/flush DNS before testing fixes
Most issues can be pinpointed to accidental record deletions or mismatches between Workspace and registrar DNS setups during account changes.
If scoring factors like IP reputation are ruled out, comparing MX record configs between Google and your domain manager is an essential troubleshooting step.
Conclusion and Summary – Key Takeaways for Google Workspace MX Records
Configuring Google Workspace MX records allows you to connect custom domains with user inboxes, route email correctly, avoid critical delivery failures, and leverage Google’s email infrastructure.
These simple DNS entries redirect messages destined for your domain away from registrar-default channels towards Google servers instead.
Carefully entering the provided records prevents unnecessary bouncebacks and spam flags. They form vital pointers towards Google mail exchanges.
